Iterator
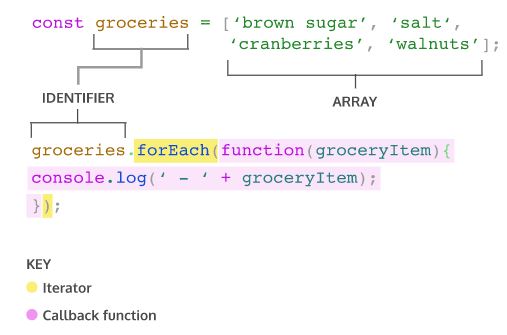
Looping을 더욱 쉽게 만들어주는 JavaScript의 built-in array methods를 iteration method(=iterator)라고 합니다. Iterator는 array가 element들을 조작하고 value를 반환하기 위해 호출하는 메서드로서 도움을 줍니다.
forEach()
forEach()는 특정 함수를 array 각각의 element들에 적용하는 iterator입니다. 보통 iterator의 인자로 함수를 받은 후, element들 각각을 인자로 사용해 해당 함수를 호출합니다. (이렇게 다른 함수의 인자로 사용되는 함수를 callback 함수라고 부릅니다.)
forEach()는 기존의 array를 변경하지 않으며, undefined를 return합니다.
groceries.forEach(groceryItem => console.log(groceryItem));
또한, arrow function을 인자로 사용해 iterator를 호출할 수도 있습니다. 이처럼, iterator의 인자로 사용되는 함수의 syntax는 임의로 자유롭게 사용할 수 있습니다.
map()
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const bigNumbers = numbers.map(number => {
return number * 10;
});
console.log(numbers); // Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
console.log(bigNumbers); // Output: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
map() 역시 forEach()와 비슷하게 동작합니다. 인자로 callback 함수를 받아, array 각각의 element를 callback 함수의 인자로 사용합니다. 다만, map()은 함수를 적용한 새로운 값들을 array에 담아서 반환한다는 점이 특징입니다.
filter()
const words = ['chair', 'music', 'pillow', 'brick', 'pen', 'door'];
const shortWords = words.filter(word => {
return word.length < 6;
});
console.log(words); // Output: ['chair', 'music', 'pillow', 'brick', 'pen', 'door'];
console.log(shortWords); // Output: ['chair', 'music', 'brick', 'pen', 'door']
filter()는 원래의 array에서 특정 조건에 만족하는 element들만 골라내어 새로운 array에 담아 반환합니다. 따라서, filter()에 인자로 사용되는 callback 함수는 반드시 boolean 값을 리턴하는 함수여야 합니다. 이 때, callback 함수가 true를 반환하게 하는 element들이 새로운 array에 담깁니다.
findIndex()
const jumbledNums = [123, 25, 78, 5, 9];
const lessThanTen = jumbledNums.findIndex(num => {
return num < 10;
});
console.log(lessThanTen); // Output: 3
console.log(jumbledNums[3]); // Output: 5
findIndex()는 특정 element의 위치를 알고 싶을 때 사용하는 iterator입니다. Callback 함수가 true를 반환하는 첫 번째 element의 index를 return합니다. 만일, callback 함수의 조건을 충족하는 element가 없다면 findIndex()는 -1을 반환합니다.
reduce()
const numbers = [1, 2, 4, 10];
const summedNums = numbers.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => {
return accumulator + currentValue
})
console.log(summedNums) // Output: 17
| Iteration | accumulator |
currentValue |
return value |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Second | 3 | 4 | 7 |
| Third | 7 | 10 | 17 |
reduce()는 말그대로 array을 감소시켜 하나의 값으로 만드는 iterator입니다. Callback 함수에 따라 array의 각 element를 accumulator에 대해 계산해, 최종적으로 하나의 계산 값을 반환합니다.
const numbers = [1, 2, 4, 10];
const summedNums = numbers.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => {
return accumulator + currentValue
}, 100) // <- Second argument for .reduce()
console.log(summedNums); // Output: 117
| Iteration # | accumulator |
currentValue |
return value |
|---|---|---|---|
| First | 100 | 1 | 101 |
| Second | 101 | 2 | 103 |
| Third | 103 | 4 | 107 |
| Fourth | 107 | 10 | 117 |
또한, reduce()는 optional한 두 번째 parameter를 받을 수 있으며, 이 때 해당 parameter는 accumulator로서 사용됩니다.